Bangladeshi weather experts said Tuesday that a deadly cyclone that carved a swath of destruction was one of the quickest-forming and longest-lasting they’d experienced, blaming climate change for the shift.
Cyclone Remal, which made landfall in low-lying Bangladesh and neighboring India on Sunday evening with fierce gales and crashing waves, left at least 38 people dead, destroyed thousands of homes, smashed seawalls and flooded cities across the two countries.
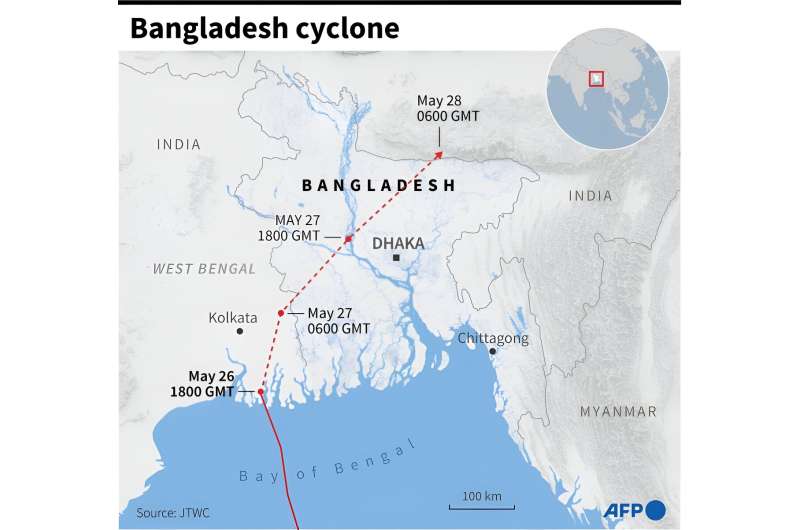
“In terms of its land duration, it is one of the longest in the country’s history,” Azizur Rahman, director of the state-run Bangladesh Meteorological Department told AFP, adding it had battered the country for more than 36 hours.
Slow-moving and longer-lasting storms bring greater destruction.
Rahman said the cyclone triggered massive rains, with some cities receiving at least 200 millimeters (7.9 inches).
Storm surges breached multiple embankments, meaning seawater flooded into farmland, damaged freshwater fish farms common along the coast, or corrupted drinking water.
Bangladesh’s state minister for disaster Mohibbur Rahman said 3.75 million people had been affected by the cyclone, more than 35,000 homes were destroyed, and another 115,000 damaged.
Meteorologist Rahman said the cyclone formed more quickly than almost all the cyclones they have monitored in recent decades.
“Of course, quick cyclone formation and the long duration of cyclones are due to the impact of climate change,” Rahman said.
“It took three days for it to turn into a severe cyclone from low pressure in the Bay of Bengal… I’ve never seen a cyclone formed from a low pressure in such a quick time,” he said.
“Usually, a cyclone is formed in the south and southwest of the Bay of Bengal, then takes seven to eight days to turn into a severe cyclone.”
The worst impact was stemmed by the expansive Sundarbans mangrove forest straddling Bangladesh and India — where the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers meet the sea, Bangladesh’s state weather department said.
The crucial sea-water coastal forests help dissipate the violence of such storms.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) warned this month that half of the world’s mangrove ecosystems are at risk of collapse due to climate change, deforestation and pollution.